
The smaller the unit square used, the higher the accuracy of the approximation. However, it is only an approximate value of the area. This method can be used to find the area of any shape it is not limited to regular hexagons.
#Surface area of a hexagonal prism formula full#
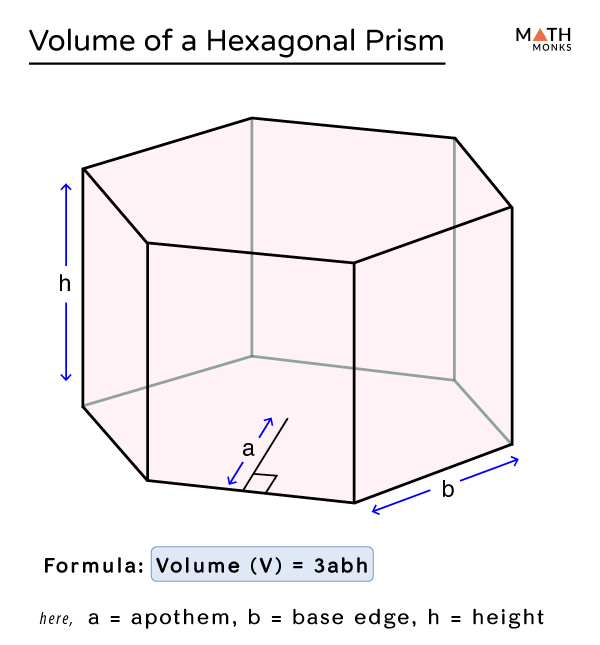
The regular hexagon to the right contains 17 full squares and 10 partial squares, so it has an area of approximately: The regular hexagon on the left contains 6 full squares and 10 partial squares, so it has an area of approximately: The grid above contains unit squares that have an area of 1 cm 2 each. Below is a unit square with side lengths of 1 cm.Ī grid of unit squares can be used when determining the area of a hexagon. The area formula using the apothem is:Īnother way to find the area of a hexagon is to determine how many unit squares it takes to cover its surface. The apothem, a, of a regular hexagon is half of the distance between opposite sides of the hexagon. In such a case, the area of the hexagon is: Sometimes, in real life, it is easier to measure the distance between opposite sides of a regular hexagon. Plugging the side length into the area formula: Given that the perimeter is 72, the length of each side of the regular hexagon can be found by dividing the perimeter by 6, making each side length 12. The area of a regular pentagon is found by \(V=(\frac\times2\times1.5)=1.5\), rewrite the equation using this product.Find the area of a regular hexagon that has a perimeter of 72. This formula isn’t common, so it’s okay if you need to look it up. We want to substitute in our formula for the area of a regular pentagon. Remember, with surface area, we are adding the areas of each face together, so we are only multiplying by two dimensions, which is why we square our units.įind the volume and surface area of this regular pentagonal prism. Remember, since we are multiplying by three dimensions, our units are cubed.Īgain, we are going to substitute in our formula for area of a rectangle, and we are also going to substitute in our formula for perimeter of a rectangle. When we multiply these out, this gives us \(364 m^3\). Since big B stands for area of the base, we are going to substitute in the formula for area of a rectangle, length times width.
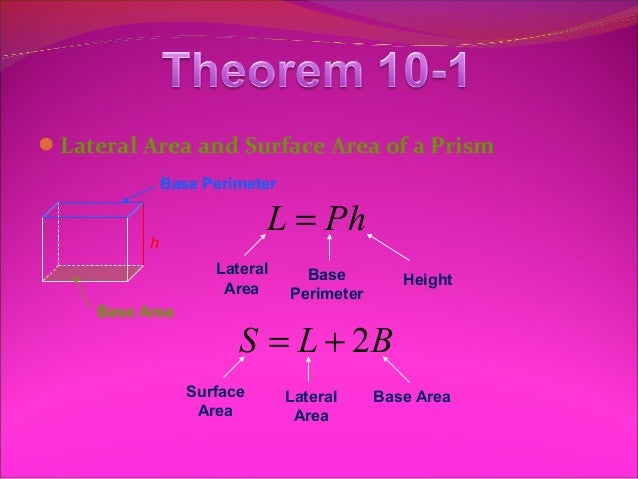
Now that we know what the formulas are, let’s look at a few example problems using them.įind the volume and surface area of this rectangular prism. The formula for the surface area of a prism is \(SA=2B+ph\), where B, again, stands for the area of the base, p represents the perimeter of the base, and h stands for the height of the prism. We see this in the formula for the area of a triangle, ½ bh. It is important that you capitalize this B because otherwise it simply means base. Notice that big B stands for area of the base.

To find the volume of a prism, multiply the area of the prism’s base times its height. Now that we have gone over some of our key terms, let’s look at our two formulas. Remember, regular in terms of polygons means that each side of the polygon has the same length. The height of a prism is the length of an edge between the two bases.Īnd finally, I want to review the word regular. Height is important to distinguish because it is different than the height used in some of our area formulas. The other word that will come up regularly in our formulas is height. For example, if you have a hexagonal prism, the bases are the two hexagons on either end of the prism. The bases of a prism are the two unique sides that the prism is named for. The first word we need to define is base.
#Surface area of a hexagonal prism formula how to#
Hi, and welcome to this video on finding the Volume and Surface Area of a Prism!īefore we jump into how to find the volume and surface area of a prism, let’s go over a few key terms that we will see in our formulas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
